Key Points
-
-
Scoliosis is a lateral deviation of the spine that may present in different forms and degrees of severity, affecting posture and body symmetry and may be accompanied by rotational torsion of the vertebrae.
-
There are three main subtypes of scoliosis classified according to their origin: idiopathic, with unknown causes but possibly multifactorial in nature; congenital, related to vertebral malformations present from birth; and neuromuscular, associated with conditions affecting the nervous system and muscles.
-
Treatment of scoliosis varies according to its severity and ranges from the use of braces and physical therapy to surgical procedures such as spinal fusion, especially in cases of pronounced curvatures.
-
Definition of scoliosis: What is it and how does it develop?
Scoliosis is defined as a lateral deviation of the spine that is normally straight. This disorder develops from an abnormal curvature that can reduce the space inside the chest, affecting posture and causing scoliosis symptoms.
Scoliosis can take various forms, such as an S-shaped curve or a C-shaped curve, and often includes rotational twisting of the vertebrae.
The causes of scoliosis can vary depending on the type of scoliosis and can disrupt posture and body symmetry by inducing rotation in the bones of the spine, resulting in asymmetrical elevation of one shoulder, shoulder blade or hip compared to the other side.
Types of scoliosis and their differences
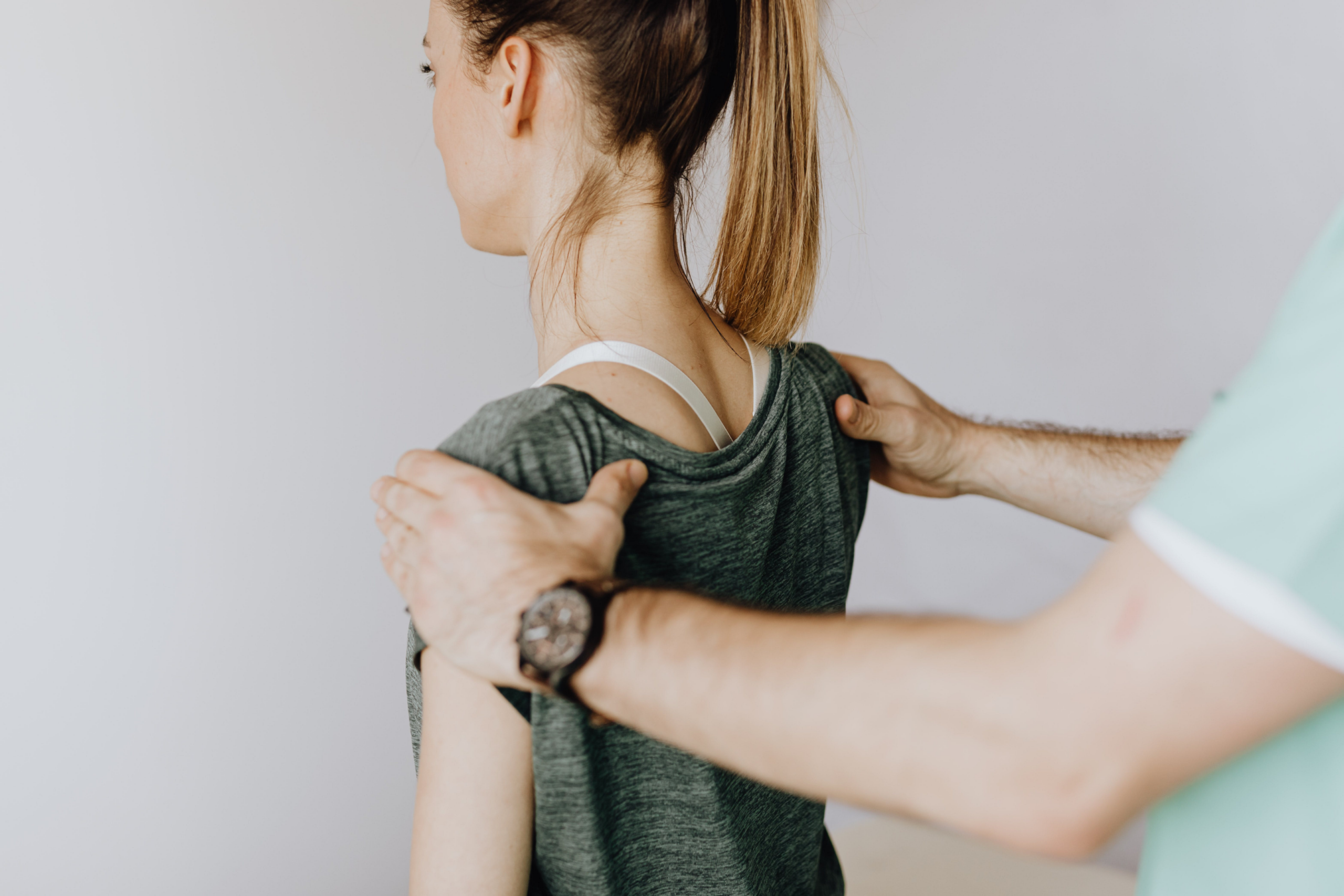

There are three subtypes of scoliosis according to its cause: idiopathic, congenital and neuromuscular. Each type presents itself in a different way, has different causes and characteristics.
Let’s take a closer look at each of these forms of scoliosis.
Idiopathic scoliosis
Idiopathic scoliosis is a spinal deformity that is approximately 2% prevalent and has no known specific cause. This condition is not related to factors such as carrying heavy backpacks, adopting poor posture, playing sports or sleeping in a certain position. It is defined by a deformity of the spine in the upper anteroposterior plane. It is believed to be a multifactorial disease involving genetic and environmental factors.
Idiopathic scoliosis is classified into three groups according to the age of onset:
-
Idiopathic infantile scoliosis
-
Juvenile idiopathic scoliosis
-
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
Congenital scoliosis
Congenital scoliosis is a condition in which the bones of an infant’s spine do not form normally before birth, which can result in a sideways curvature of the spine. If the spine does not form properly, it can cause congenital scoliosis. Although the precise causes of congenital scoliosis are unknown, some hypotheses have been formulated that include the pregnant woman’s exposure to toxins, gestational diabetes or the ingestion of certain medications during pregnancy.
Congenital scoliosis can have a significant impact on a child’s growth and development, as the abnormal structure of the spine can lead to imbalances and complications in physical development.
Neuromuscular scoliosis
Neuromuscular scoliosis is one of the three primary types of scoliosis, identified by an unusual side-to-side S- or C-shaped curvature of the spine.
It develops as a consequence of diseases that impact the nervous system and affect the muscles, including conditions such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy and spina bifida.
Neuromuscular scoliosis is directly related to neuromuscular diseases such as muscular dystrophy and cerebral palsy. These conditions can cause muscle weakness and imbalance, leading to the development of curvature in the spine.
Common symptoms of scoliosis

Initial symptoms of scoliosis may include asymmetry in the shoulders, prominence of one shoulder blade over the other, and unevenness in the waist with one side higher.
In the case of children, these signs may be visibly evident, along with a rib prominence and a noticeable curvature of the spine.
In severe scoliosis situations, the spinal deformity may reach such a degree that the rib cage puts pressure on the lungs, resulting in respiratory distress for the patient. This problem may affect the patient’s quality of life and require medical treatment.
Adults with scoliosis are more likely to experience chronic back pain compared to individuals without scoliosis.
Proper treatment can help control the progression of scoliosis and relieve pain.
Diagnosis of scoliosis: process and tests used
The diagnosis of scoliosis is made by physical examination, which includes looking for signs such as lateral deviation of the spine, back pain or low back pain, weakness or tiredness in the spine after standing or sitting for long periods.
This process is complemented by a detailed medical history that takes into account the family history that may influence the prevalence of the disease. To carry out this process, the physician diagnoses scoliosis through a series of tests and evaluations.
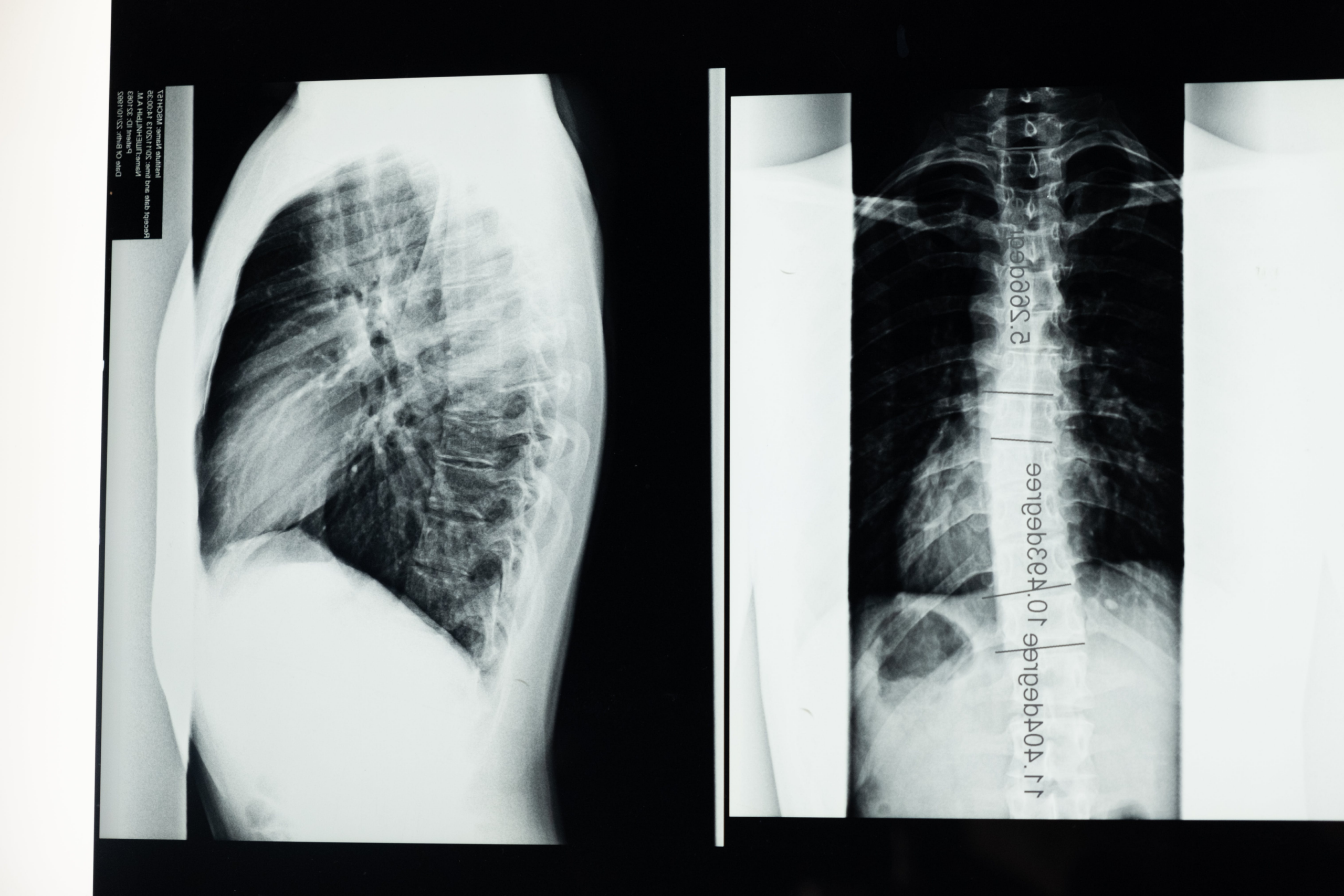
Conventional X-rays are used to validate the diagnosis of scoliosis and assess the extent of spinal curvature. The image provided by X-rays allows physicians to assess the severity of scoliosis and plan appropriate treatment.
Imaging tests such as MRI and CT scans provide more detail about the severity of the spinal curvature and help confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment options for scoliosis
The process of treating scoliosis depends on the severity of the curvature and the age of the patient. Treatment options can range from non-surgical measures, such as the use of braces and physical therapy, to surgical interventions in more severe cases.
Let’s take a closer look at each of these options.
Non surgical treatment: Corsets and physiotherapy
The orthopedic brace is used to correct the deviation of the spine, representing the first step in the non-surgical approach to idiopathic scoliosis, being prescribed by a medical professional.
On the other hand, chiropractic plays a crucial role in the treatment of scoliosis; it helps to improve the curvature, strengthens the back muscles and promotes better posture through specific exercises.
Chiropractic can be a complementary approach in the treatment of scoliosis, but it is important to understand that it cannot definitively “cure” scoliosis.
Here are some ways chiropractic can help people with scoliosis:
1. Muscle Tension Reduction and Pain Relief
2. Improvement of Joint Mobility
3. Focus on Neuromuscular Function
4. Posture and Exercise Education
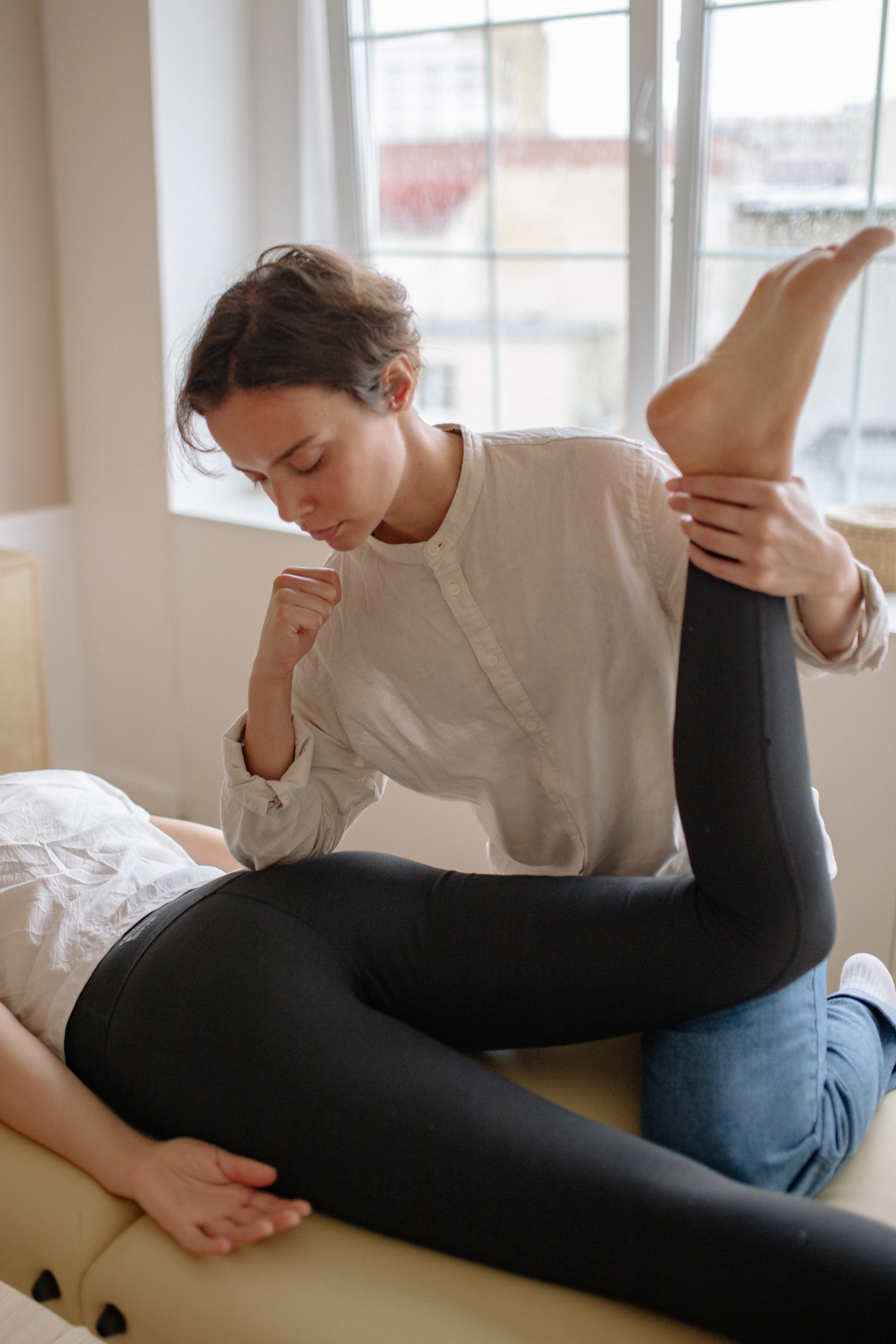

It is crucial to note that chiropractic treatment should be part of a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach to scoliosis. It is important to work closely with other healthcare professionals to develop a treatment plan tailored to the individual needs of each person with scoliosis.
Scoliosis Surgery: Indications and Procedures
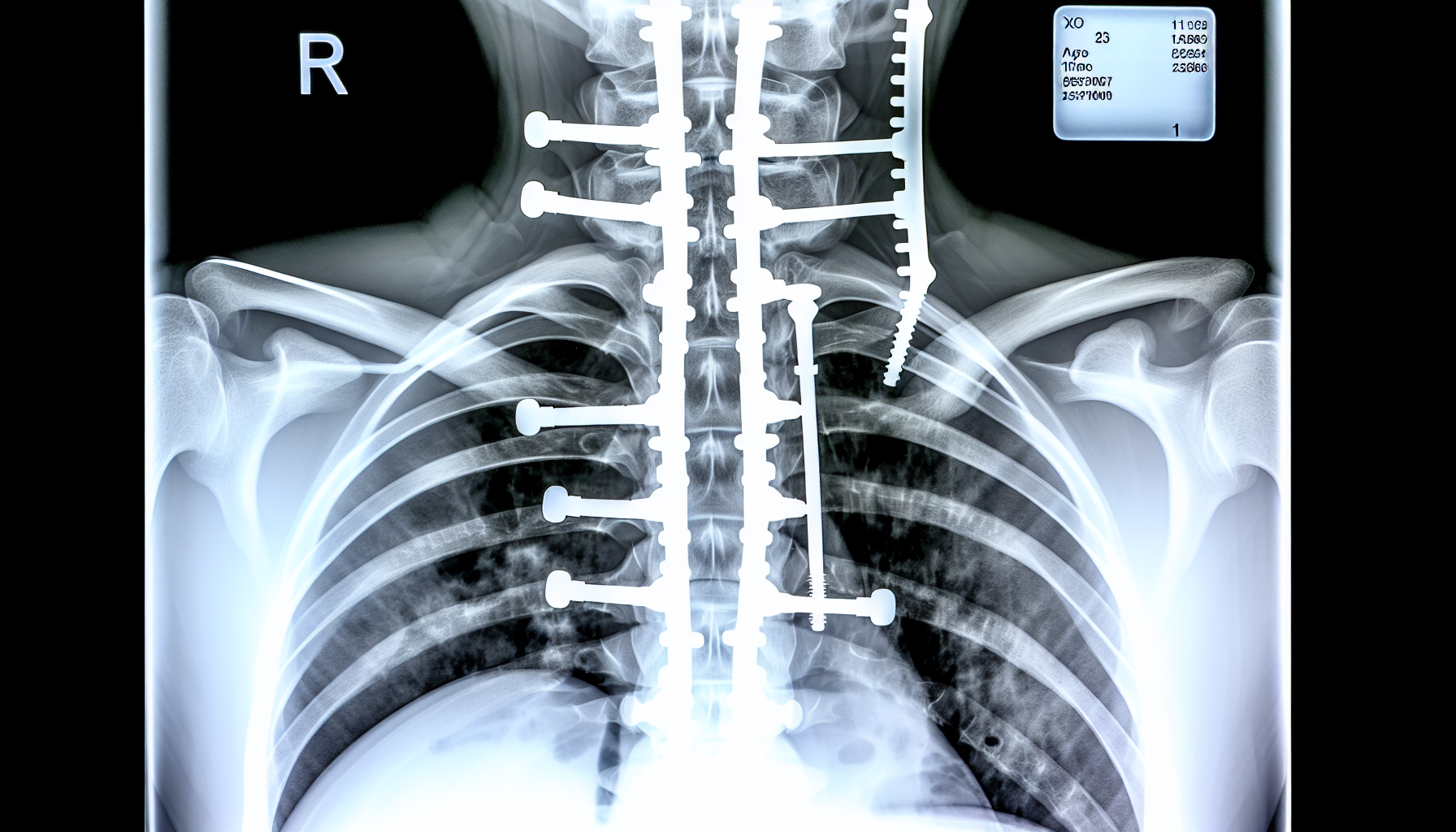
In some cases, when the curvature is very pronounced, surgery may be recommended. The criteria for scoliosis surgery are based on the extent of the spinal deformity and the location of the curvature.
The purpose of surgery to correct scoliosis is to straighten the spine and align the shoulders and hips to resolve the back condition. However, we will place special emphasis on prevention to avoid getting to this point.
Prevention and care in the management of scoliosis
Although there are no known specific preventive measures for scoliosis, early detection and regular follow-up are essential for proper management and avoidance of long-term complications. Clinical spinal examination and radiography are the main methods for early detection of scoliosis, allowing for proper follow-up and management from the onset.
Long-term complications of untreated scoliosis may include an increase in the degree of spinal curvature, loss of flexibility, breathing difficulties and progressive pain.
Therefore, it is important to maintain proper posture, perform back strengthening exercises such as swimming, take care of postural hygiene, prevent overweight and engage in regular physical activity.
Summary
In summary, scoliosis is a condition that can have a significant impact on people’s lives if not managed properly. Although there is no definitive cure, there are several treatment options available that can help patients live a full and healthy life. Early detection and regular follow-up are key to preventing serious complications and improving the quality of life for patients with scoliosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is scoliosis and why does it occur?
Scoliosis is a lateral deviation of the spine, which can be caused by problems in the nervous system or by deviations in the formation of the vertebrae and ribs in infants.
How to prevent scoliosis?
Scoliosis prevention focuses on maintaining good posture, regular exercise to strengthen the back and core, ergonomics in the work environment, weight control, regular medical checkups, avoiding poor postural habits, moderating the use of electronic devices and increasing awareness of the importance of spinal health.
Medical care and professional counseling are essential to address any genetic predisposition or underlying medical conditions.
What are the best exercises if I have scoliosis?
For people with scoliosis, exercises can be beneficial to strengthen the back, core and improve flexibility.
Back stretches, core strengthening exercises, controlled rotational movements, activities such as Pilates, yoga and swimming, as well as stability exercises with an exercise ball, can be considered.



